What are Options in Finance?
Options are financial contracts which allow the buyer a right, but not an obligation – like in the case of futures or stocks, to buy or sell an asset on a specific date at a specific price called strike price which is predetermined at the date when the option is being bought or sold.
The popularity of Options has surged over the last few years.
You will agree with this statement once you read the statistics provided by the Options Industry Council.
- The year 1973: Volume of options traded = 1 Million
- The year 2015: Volume of options traded = 5 Billion
That’s a huge leap. Anybody interested in Trading Option? This is an awesome route to diversify your Portfolio.
However, your first step should be understanding what are Options in Finance? So in this article, we will be focusing on the nuts and bolts of Options.
- What are Options in Finance? – Infographics
- What are Options in Finance – Book vs Analogy?
- Parties to the Option Contract
- Underlying Assets in Options
- Call and Put Options
- What are Options Types
- What are Options Contract
- Why Trade Options?
- Steps for Options Trading
- Disadvantages of Options Trading
- Beware of the Option Risks!
What are Options in Finance? – Infographics
What are Options in Finance Book vs Analogy
We will try to break down “What are Options in Finance” in two ways: 1) What the Books say! 2) How I like to Decode them!
#1 What the Books say about what are Options in Finance!
- Options are a type of financial derivative. They represent a contract sold by one party to another party.
- Options contracts offer the buyer the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell a security or other financial asset.
- It includes an agreed-upon price during a certain period of time or on a specific date.
- In simple terms, the Buyer can exercise the contract only if he feels that he is going to benefit.
- If he thinks that he is going to make a loss in the transaction, he simply can let go of the contract by not exercising it.
- This explains the term “Right but not the Obligation”.
- On the other hand, the Seller of the option has the obligation to carry out the transaction if the holder chooses to exercise it.
#2 How I like to Decode What are Options in Finance?
Understanding what are Options in Finance can be intimidating at first. Even I had a tough time when I started first. But don’t worry. You can find the underlying idea behind an option in many simple things. Let’s discuss one analogy for the same.
The Party Planners Analogy:
- Say, for example, you discover Party Planners for your Parents 25th
- Unfortunately, you don’t have the entire down payment to pay them until the next 2 months.
- You talk to them and negotiate terms. The agreement is settled on paying an initial amount of $500 for booking and paying the remaining amount of $3000 later.
Now consider 2 scenarios:
Now consider 2 scenarios:
Scenario 1: Having The Right!
- Later you learn that Party Planners have arranged birthdays of Celebrities and have now raised their prices to $5000.
- In this case, you still pay them the earlier promised amount of $3000 as you have the right for the same.
Scenario 2: No Obligation!
- You learn that the Party Planners are poor in their Planning and Organizing through word of mouth.
- In this case, you don’t have to go forward with them, as you don’t have the obligation to.
- But you lose your earlier paid amount of $500. You don’t mind the same as you are able to save your Parents Party.
This is similar to how Options work. You have the right but not the obligation to exercise them. Let’s now discover some important terms and concepts of Options trading.
Parties to the Option Contract
An Option Contract consists of the following two parties:
- Holder: Buyer of the Contract
- Writer: Seller of the Contract
When the Holder of the option contract chooses to initiate the transaction, he is said to be exercising the option.
When the holder does not initiate or exercise the contract, then the contract eventually expires.
Underlying Assets in Options
ng a form of derivative, Options derive their value from an underlying asset. So what are these underlying assets?
- Stocks
- Bonds
- Indices
- Foreign currencies
- Commodities
- Basket options (collection of different assets)
Call and Put Options
Key to understanding what are options in Finance is to know what are Calls and the Puts!!!
- A call option gives the holder the right but not the obligation to buy an underlying asset at a specified price and a pre-determined date.
- A put option gives the holder the right to sell an underlying asset at a specified price and a pre-determined date.
What are Option Types
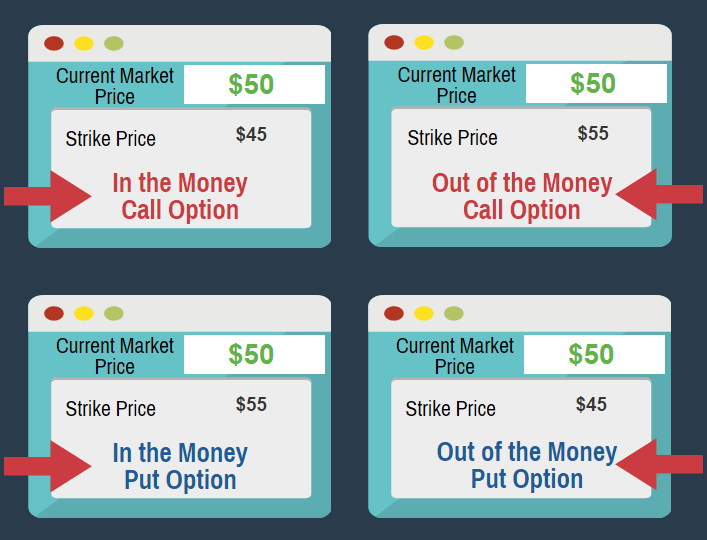
1. In the Money Call Option:
The call option is in the money when the current market price is above the strike price.
2. Out of the Money Call Option:
The call option is out of the money when the current market price is below the exercise strike price
3. In the Money Put Option:
The Put option is in the money when the current market price is above the strike price.
4. In the Money Call Option:
The Put option is out of the money when the current market price is below the strike price.
What are Options Contract?
#1 Contract Size
- Contract size means the amount or the number of underlying assets covered by the option contract.
- Let’s say that the underlying asset is Stock/Shares and one contract includes 100 shares.
- So when the holder exercises one option contract, 100 shares will change hands.
#2 Strike Price
- Strike Price is the pre-determined Buying or Selling price for the underlying asset if the Option is exercised.
- For Call Option, the strike price is the one at which the security can be bought.
- For Put Option, the strike price is the one at which the security can be sold.
So what is the relation between the strike price and the market price of the Security?
The answer is Profit.
If the option is exercised, then the difference between the current market price and the strike price is the amount of profit made.
#3 Premium
- To acquire the Option, you need to pay a certain price.
- This price, also known as the option price is called the premium.
Options Premium has two main components:
Options Premium has two main components:
Intrinsic Value:
Don’t get daunted by the term intrinsic value, it’s easy to understand.
Intrinsic value is the difference between the underlying price and the strike price.
Let’s present it with the help of formula to understand it better.
Intrinsic Value: Call Option
For Call Options, this is how you will calculate the Intrinsic Value:
Intrinsic Value= Current Stock Price – Strike Price
Intrinsic Value: Put Option
For Put Options, this is how you will calculate the Intrinsic Value:
Intrinsic Value= Strike Price – Current Stock Price
Time Value
So let’s now understand what time value is.
- Suppose you buy an option with a strike price of $100. But unfortunately, its price goes down to $90.
- Now, in this case, you will not exercise your option, because you will be at a loss.
- But in 1 or 2 months the prices are expected to rise to $105. So, in this case, you will make a profit of $10 if you hold it for another month.
- For this, you might have to pay an extra $5 to hold your contract. This extra $5 is your Time value.
So long story short:
Time value is the amount that you are ready to pay with the hope that the market might move in your favour.
Option Premium Formula:
Now understand this formula for Option premium:
Premium= Intrinsic Value + Time Value
So in our case, the option premium comes to:
Premium = $10 + $5 = $15
Factors affecting Option Premium
There are various factors that may affect the options premium. Some of them are:
- Price may either increase or decrease. Changes in the price lead to an increase or decrease in the premium.
- Strike Price plays a major role in determining the intrinsic value of the option. The more the option becomes in the money, the more the premium increases. Similarly, it decreases when the option becomes out of the money.
- Volatility is the measure of the risk or the variability in the price. Hence you can say that the higher the volatility, the greater the expected fluctuations in the price and vice-versa.
Why Trade Options?
Given the choice, the majority of us will opt for buying stocks than buying options. Opting trading is considered a bit more complicated but they can give you the benefits that stocks cannot give.
Following are some reasons as to why Options are beneficial:
Cost Advantage
To understand this let’s take an example of Buying a Stock and Buying Call Options on the same stock. You will be able to see how the returns generated vary.
Out of box Returns
From the above example, we have understood the vast difference in the return percentage. Buying a Stock gave us the overall return of 10% whereas with buying an Option, the returns shooted to 60%.
Leveraged Gains
Options enable you to put in less money and obtain the additional gain.
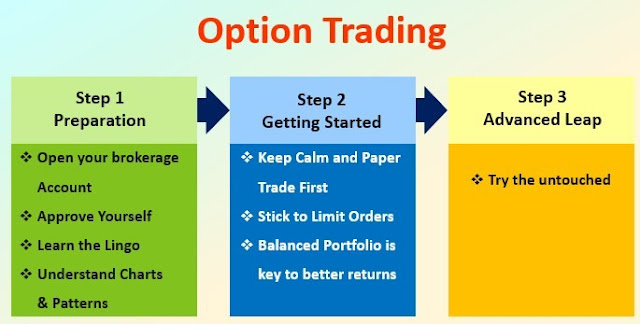
Steps for Options Trading
Now that you have understood what are options in Finance, let us look at Options Trading.
There are three major milestones of Options Trading.
- Preparation
- Getting Started
- Advanced Leap
Step 1: Preparation
Starting with the first step, you will do all the required preparations as follows:
Open your brokerage account:
To enter your trading transactions, you need your brokerage account. Open the same and make sure you do some initial research to find out the best account for yourself.
Approve Yourself:
Get yourself approved by the Securities and Exchange Commission as per the options trading requirements put forth by them.
Learn the Lingo:
Get yourself acquainted with all the Options trading terminologies. This will help you in understanding the process easily.
Understand Charts & Patterns:
Once you start Trading, you are definitely going to pay a lot of attention to the Price Movements. So to know how this works, it necessary to get hands-on technical analysis knowledge.
Step 2: Getting Started
Keep Calm and Paper Trade First
To strike the iron when it’s hot, you need to know the temperature at which it gets hot. Similarly, for trading options, first, understand its nuances. Start first by Paper trading, know how much are your returns and then proceed further.
Stick to Limit Orders
Limit orders set the maximum and minimum limit at which you are willing to buy or sell. This also helps you to maximize your returns.
Balanced Portfolio is the key to better returns
This is just as the old saying “Don’t hold all the eggs in one basket”. Similarly, make sure that all the options are not Call or Put. Balance both the types to maximize your returns.
Step 3: Advanced Leap
Try the untouched
Once you are confident and are considering making some good returns, move forward with some advanced level strategies. Make sure you know your statistics well before taking this step.
Disadvantages of Options Trading
Time Sensitive Investments
Since the contract is for a short period, you may lose your entire investment even with a correct prediction of the market direction.
Higher Commissions
When you compare the commissions for a normal Stock and an option you will find a large difference. Yes, commissions for Options are higher.
Complexity of Operations
Options and Strategies are not easy. They may become complicated for novice investors.
Time Decay Factor
Many times options expire worthlessly. Again this is the effect of the time-sensitive nature of the options.
Beware of the Option Risks!
Now that you have a basic understanding of What are Options in Finance and Options Trading, let us look at Options Risks. Remember that, there are two sides to the same coin. Just as there are many advantages to trading options, there are also various risks involved.
Wasted Asset if not exercised!
Options come with a Limited life as they have an expiry date. Thus if they are not exercised they are a wasted asset.
Leverage may Backfire
Although the initial capital required may be low but even small market movements can have a large impact on the Option Contract. Also, have a look at Financial Leverage.
Losses may Mountain for option “Writers”
It is seen than option writers are at greater risks than the option holders. They receive a limited and fixed amount of premium but the loss can be unlimited.
Options Liquidity at stake
There are different types of options, which may pose a problem of low liquidity for each type. This may cause a problem to make the required trades at the right prices.
What are Options in Finance – Know what you want
I would say that you have a clear idea of what you want to accomplish before you actually start trading options. You may want to earn more income or increase the value of your portfolio.
Once you know what your goal is, you can easily narrow down appropriate strategies.
So Start your Options Trading with these three words:
Learn, Apply, Master!!!


No comments:
Post a Comment