
Offshoring Definition
Offshoring can be defined as a practice of processing business operations from one country to another country usually from developed industrialized countries to less-developed/developing countries with the motive of cutting down the cost of doing business, enjoying tax benefits, and complying with less stringent regulations.
Explanation
- There are individual banks that offshore their back-office functions to other countries that provide an efficient and cheap workforce.
- Manufacturer offshore the first stage of production of goods in another country where the raw material and labour cost is cheap and keeps finished products in its own country.
- Labour services of staffing agencies offshore to other countries.
- Goods are imported from foreign markets to domestic markets by the retailers.
- Import Inputs and raw materials from cheaper markets.
Evolution
- First offshoring dates back to the 1960s when in the developed world jobs in the manufacturing sector moved out of the country to the overseas market than in the 1970s; the service sector jobs were outsourced to different countries.
- Primarily factories got transferred from developed to developing countries, which caused a structural change in the world from industrial to post-industrial society.
- Reduced cost of transportation and communication during the 20th century with a higher difference in pay rates made offshoring an easy option. Then with the growth of the internet, fibre optics and world wide web offshoring became a usual practice.
Causes
- To stay away from protectionism and making full utilization of free trade areas in the overseas market.
- To reap the benefits of cheap labour cost as it is low in offshore markets.
- To make full utilization of resources available.
- To supply goods and services in international markets for the targeted audience.
- To get skilled and efficient workforce supply.
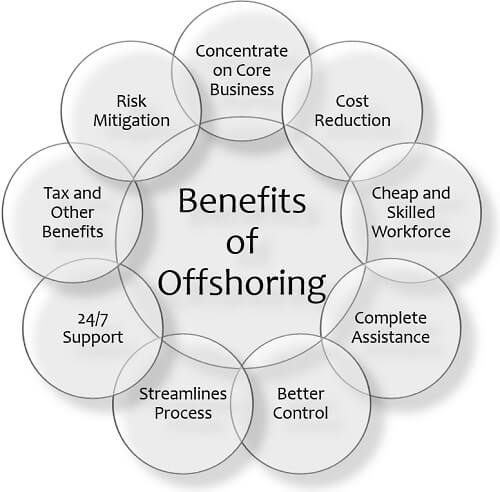
Importance
- Companies that offshore their businesses may offer their services and products at lower rates, but still, they earn huge profits as the cost of production gets cheaper.
- The resources that are not available in the internal market can be accessed easily in the international market with the help of offshoring.
- Processes that are offshored like customer service, information technology, software development, etc. will be handled by experts; hence the problem of talent shortage and a specific skill can be dealt with.
- Focus on main business activity can be maintained as the back-office task can be offshored. This leads the company head to focus on core business and improve productivity and output quality.
- New technologies can be embraced to speed up the process of business, which helps in making the best use of investment with the least interruption.
- With this help of business risk management can be easily done at the time of technical crisis, natural calamities, or market fluctuations. The other part of the company will have things in a proper place to respond rapidly to any uninvited situation.
- Consumers also get benefited when offshoring a business due to affordability as they can save more money, which in turn will increase the value of the company in the economy.
- This globally also provides a wider talent base that leads to the utilization of new skills, innovative strategies, and new capabilities.
No comments:
Post a Comment