Hedge Fund Definition
A hedge fund is an aggressively invested portfolio made through a pooling of various investors and institutional investor’s fund and invests in a variety of assets which generally is a pool of assets providing high returns in exchange of higher risk through various risk management techniques and hedging techniques.
Explanation
To invest in them you need Money like Bill Gates and to manage them you need Brains like Einstein. Hedge funds have been in the limelight due to various strategies used and some amazing returns generated. They have confronted the traditional fund sector with a strong challenge. They have attracted more attention and media interest than the traditional sector. You must have also heard a lot about Hedge funds.
They have been successful in getting the pool of talented fund managers due to their lucrative compensation packages. Over the years, they have attracted a very strong flow of capital.
You can say that the Hedge Fund is a type of pooled investment. But isn’t Mutual Fund the same? So what makes Hedge Fund different than the others?
The major difference is:
Investment in Hedge Funds is open only to a limited group of investors and its performance is measured in absolute return units.
If you go by the nomenclature of Hedge Funds, the term Hedge (Hedging) literally means lowering the overall risk. This is usually done by taking an asset position that helps in offsetting the existing risk.
How does Hedge Funds work?
- It takes both Long & Short Positions.
- It uses Arbitrage.
- It includes buying and selling of undervalued securities as well.
- It trades options or bonds.
- And basically invests in any opportunity that exists in the market.
- So you can say that its primary aim is to reduce volatility & risk and to preserve capital.
While we are talking about reducing risks, you may be amazed to know how the Hedge funds do it. For doing so, they use a variety of instruments and amazingly weird strategies too. They are also flexible in their investment options.
What I mean by this is that they can use short selling, leverage, derivatives such as puts, calls, options, futures, etc.
Well, that’s a lot of different things in one sentence. So let’s now move forward and take a look at its characteristics.
Hedge Funds Characteristics
One common and frequent thing that you will notice about Hedge funds is that they vary enormously in terms of investment returns, volatility, and risk.
- Some of them have the ability to deliver non-market correlated returns.
- Major investors in Hedge funds are Pension funds, endowments, insurance companies, private banks, and high Net Worth, individuals, and families.
- Hedge Funds are managed by experienced investment professionals.
- They are illiquid investments.
- They have little to no regulations.
- They are known to use Aggressive Investment Strategies.
Hedge Funds Organization Structure
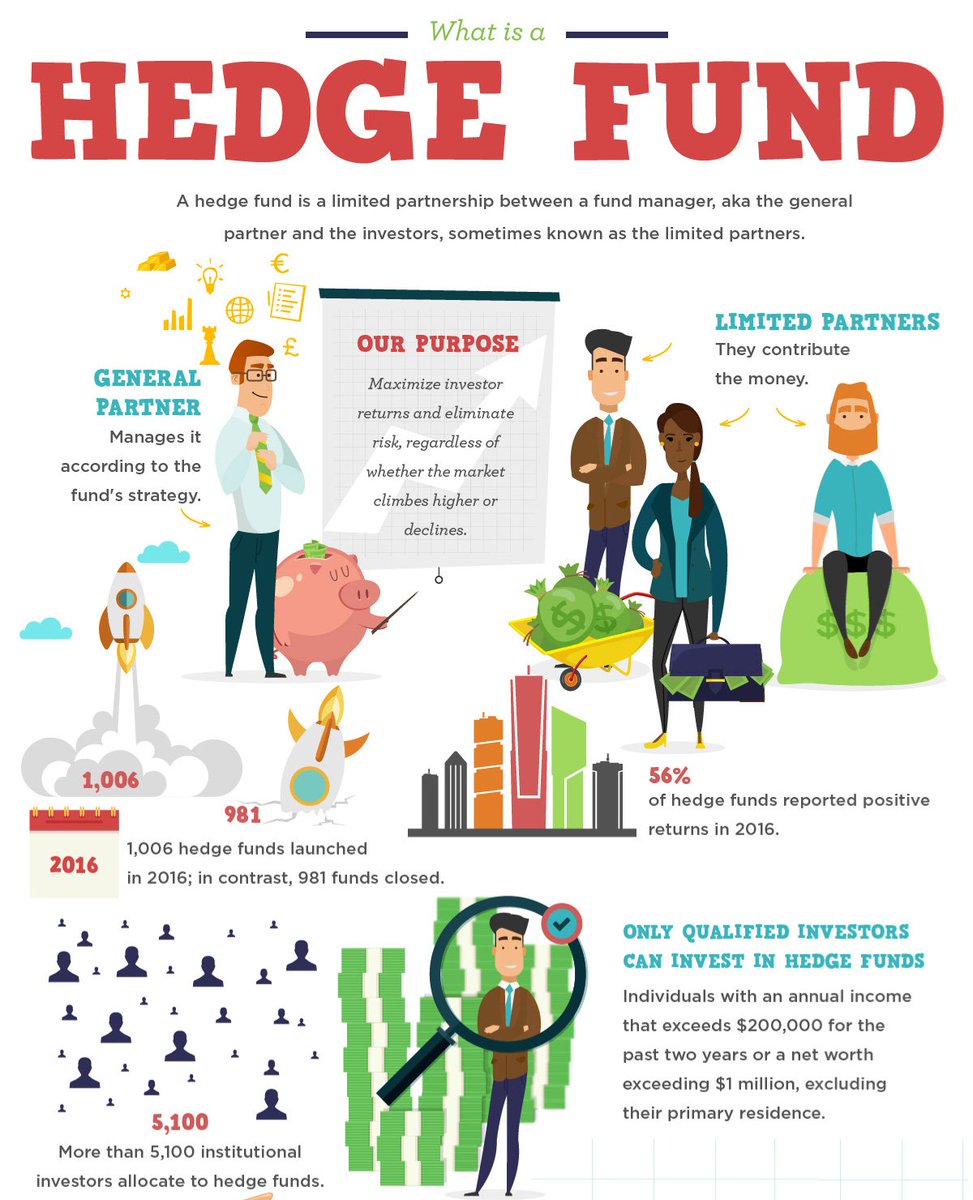
- The major organizational structure that you will find for Hedge Funds is the one with a General/Limited Partnership Model.
- The General Partners here are involved in undertaking the responsibility of managing the fund whereas the Limited partners are involved in making investments to the partnership. The limited partners are however liable only to their paid-in capital amounts.
- Also, the Typical structure used for the General partners is the Limited Liability Company. A Limited Liability Company is a flow-through tax entity and investors are limited in liability to the amount of their investment.
Hedge Funds Fee Structures
Hedge Fund Managers are compensated with two types of Fees:
- Management Fee
- Performance-based Incentive Fee
A Management fee is measured by Asset under Management and is usually calculated as a percentage of the size of the fund. This fee can be anywhere from 1-4% of net assets under management, however, 1-2% is the most common range seen.
The Performance-based incentive fees can be 15%-20% of the Profit that the Hedge Fund makes.
Due to the High Incentive-based fees, the hedge Fund Managers are always seen to be aiming at the absolute returns rather than just beating the benchmark returns.
Investors in Hedge Funds
Following are the major investors in Hedge funds:
- Pension Funds
- Charitable Foundations
- University Endowments
- High Net Worth Individuals
Hedge Funds Strategies
The varied range of hedging strategies is available to hedge funds. Some of them are listed below:
- Long/Short Equity
- Market Neutral
- Merger Arbitrage
- Convertible Arbitrage
- Capital Structure Arbitrage
- Fixed-Income Arbitrage
- Event-Driven
- Global Macro
- Short Only

No comments:
Post a Comment