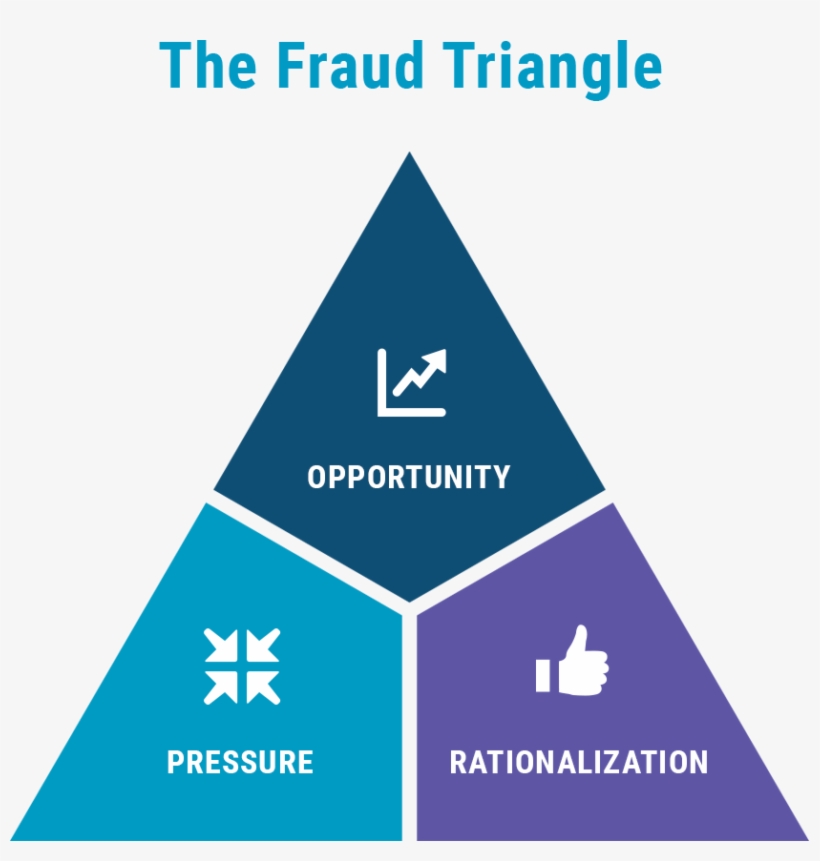
What is Fraud Triangle?
The 3 Elements
#1 – Pressure
The pressure is the motivation behind fraud committing, and that can be either personal financial pressure or pressure from superiors. Both the pressures give the motivation for committing fraud. If the pressure remains unsolved by rational & legal means, then individuals might go for irrational ways. Some common examples of personal financial pressure are un-sharable financial problems, shortage of revenue, pressure from banks to pay loans, and maintenance of lifestyle. And some examples of pressure from superiors are window dressing of accounts, teaming and leading, inventory pilferage and selling, sharing secret information with competitors for earning money, etc. When a person cannot see the apparent path of achieving personal or work goals by honest means, he or she may adopt dishonest alternatives.
#2 – Opportunity
When pressure is present employee looks for an opportunity for committing the fraud. For example, if there is no internal control over the inventory room, then the employee finds the chance to pilferage it and sell it in the market. It can be done by abusing the position, for example, pressure by superior to subordinate to show accounts by window dressing.
#3 – Rationalization
It is the last stage in the fraud triangle. This stage requires fraudsters to justify fraud in an acceptable way. Most fraud committers do not see themselves as criminals; instead, explain the situation of committing fraud. Similarly, fraud by management gives reason for performance and pressure from shareholders for dividends and all.
Challenges
- Strong Internal Control – To Prevent organization and management from committing fraud, there must be robust internal control and compliance of law and high penalties for committing fraud so that it can be reduced.
- Favourable Employee Policies – There must be favourable employee policies so that employees in need can get finance from the company instead of committing the fraud.
- Strong Fraud Deterrence Policies – There must be strong fraud deterrence policies so that employee does not even think of committing fraud because of its substantial consequences.
- Ethical Training – There must be proper ethical training to all employees, which teaches them that ethics are most important in life, and doing fraud or cheating in any situation is unethical, which helps to change the mindset of fraudsters.
Which is an Important Element?
Fraud triangle has three elements – Pressure, opportunity, and rationalization, and the most crucial factor is an opportunity. It is so because the opportunities available for committing the fraud give motivation to the fraudsters to commit the fraud. If there are strong controls in the organization and rigid policies and proper and crystal-clear reporting policies, then fraudsters might not get the opportunity to commit the fraud, and hence no fraud can take place.
How Can the Fraud Triangle Help to Identify Fraud and Avoid it?
- The motivation for committing fraud can be varying from financial to non-financial. For preventing fraud, companies must implement strong internal controls. As an organization with strong internal control experience lower frauds and quickly identify frauds.
- Strong Fraud deterrence policies also help to prevent fraud as employees have a fear of its consequences like the loss to the job and not getting a job anywhere.
- In audits, management audit and operational audits to be motivated so that management fraud can be detected.
- In the case of the statutory audit, there is a clause where the auditor has to report whether fraud is committed by employees or management or a third party.
Importance
Fraud triangle comprises three components pressure, opportunity & rationalization. It helps in preventing the frauds if there is:
- Zero Tolerance – Zero tolerance on errors and mistakes. Many employees pity themselves after committing the fraud, and for this also, organizations shouldn’t be kind and have zero tolerance for this.
- Surprise Visits and Audits – There must be a system of surprise checks, and visits by top management and auditors should also do surprise audits to ensure that no frauds are committed by or on the company.
- Code of Ethics – Companies have a robust code of ethics to ensure that they send the right message to employees when it comes to fraud. And provide that code of ethics to be followed by one and all.

No comments:
Post a Comment